Real-Time Integration: Unlike polling APIs that require you to repeatedly check for updates, webhooks deliver event data instantly as it happens, making your applications more responsive and efficient.
What are Webhooks?
Webhooks are user-defined HTTP callbacks triggered by specific events in AhaSend. When an event occurs—such as an email being delivered or bouncing—AhaSend automatically sends a POST request to your webhook URL with detailed event data. This enables you to:Automate Workflows
Trigger actions in your application when emails are delivered or bounce
Monitor Performance
Track email engagement in real-time without manual checking
Update User Interfaces
Show delivery status updates to users immediately
Handle Errors
Respond to delivery failures or suppression events automatically
How Webhooks Work in AhaSend
Delivery Guarantee: AhaSend retries failed webhook deliveries up to 6 times over 16+ minutes. Only HTTP status codes 200-299 are considered successful.
Available Webhook Events
AhaSend supports webhooks for various event types. You can choose which events to receive when configuring your webhook:Message Events
Message Events
Track the complete lifecycle of your outbound emails:
- Message Reception - Email received and queued for delivery
- Message Delivered - Email successfully delivered to recipient’s server
- Message Deferred - Temporary delivery delay (will retry)
- Message Failed - Permanent delivery failure after retries
- Message Bounced - Bounce notification received from recipient’s server
- Message Suppressed - Email blocked due to suppression list
- Message Opened - Recipient opened the email (requires tracking enabled)
- Message Clicked - Recipient clicked a tracked link (requires tracking enabled)
Suppression Events
Suppression Events
Monitor when email addresses are automatically suppressed:
- Suppression Created - New suppression added due to delivery issues
Domain Events
Domain Events
Receive alerts about domain configuration issues:
- DNS Error Detected - Problems with SPF, DKIM, or DMARC records
Understanding Message Lifecycle
The message lifecycle helps you understand when different webhook events occur:Successful Delivery Path
- Reception: Email accepted and queued for delivery
- Delivered: Successfully sent to recipient’s mail server
- Opened: Recipient opens email (requires tracking enabled)
- Clicked: Recipient clicks tracked links (requires tracking enabled)
Bounce Scenarios
Hard Bounce (Immediate Failure)
Hard Bounce (Immediate Failure)
Soft Bounce with Recovery
Soft Bounce with Recovery
Soft Bounce with Final Failure
Soft Bounce with Final Failure
Suppressed Email
Suppressed Email
Creating Webhooks
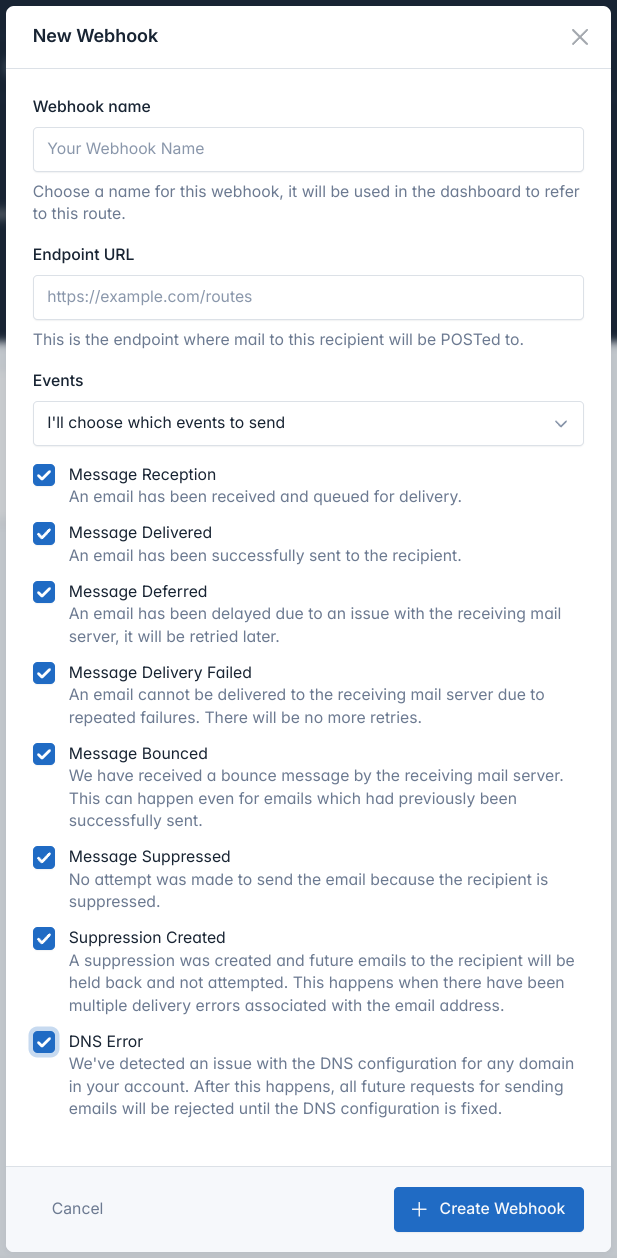
Access Webhooks Dashboard
- Log in to your AhaSend Dashboard
- Navigate to the Webhooks section from the main menu
- Click the “Add Webhook” button
Configure Webhook URL
Enter Your Endpoint URL:
- Provide the complete URL where you want to receive webhook events
- Must be a valid HTTPS URL (HTTP allowed for development)
- Should respond with 2xx status codes for successful processing
Select Events
Choose which events to receive:Option 1: All Events
- Select “Send all events to this endpoint URL”
- Simplest option, receives every event type
- Good for comprehensive logging or analytics
- Select “I’ll choose which events to send”
- Pick individual event types you need
- More efficient for targeted use cases
Testing Your Webhooks
Verify your webhook integration works correctly before going live:Use Test Events
- Go to your webhook details page in the dashboard
- Click “Send Test Event”
- Select which event types to test
- Click “Send Test Events”
Security and Verification
AhaSend follows the Standard Webhooks specification for secure webhook delivery:Security Headers
Every webhook request includes security headers:webhook-id
webhook-id
Unique event identifier - Use as an idempotency key to prevent processing duplicate events from retries.
webhook-timestamp
webhook-timestamp
Unix timestamp when the webhook was sent - Use to reject old webhook attempts.
webhook-signature
webhook-signature
HMAC signature of the payload using your webhook secret - Verify this to ensure authenticity.
Signature Verification
Use Standard Webhooks libraries for easy verification:Standard Webhooks Libraries: AhaSend webhooks are fully compatible with Standard Webhooks libraries available for Python, JavaScript, Go, PHP, Ruby, Java, Rust, C#, and Elixir.
Webhook Payload Structure
All AhaSend webhooks follow the Standard Webhooks payload format:Message Event Example
Suppression Event Example
Best Practices
Reliability and Performance
Reliability and Performance
Handle Retries Gracefully:
- Use
webhook-idas an idempotency key to prevent duplicate processing - Store processed webhook IDs to detect and skip duplicates
- Return 2xx status codes quickly (under 10 seconds)
- Acknowledge receipt immediately with 200 OK
- Queue heavy processing for background workers
- Avoid database operations that could timeout
- Log webhook processing times and errors
- Set up alerts for failing webhooks
- Track webhook-related application metrics
Security Implementation
Security Implementation
Always Verify Signatures:
- Use Standard Webhooks libraries for verification
- Reject requests with invalid or missing signatures
- Check timestamp to prevent replay attacks
- Use HTTPS URLs for production webhooks
- Don’t expose webhook URLs publicly
- Consider IP whitelisting if needed
- Store webhook secrets in environment variables
- Never commit secrets to version control
- Rotate secrets periodically
Error Handling
Error Handling
Graceful Failure Handling:
- Return appropriate HTTP status codes
- Log webhook processing errors for debugging
- Implement circuit breakers for external dependencies
- Handle unexpected event types gracefully
- Validate event data before processing
- Don’t assume all fields will always be present
- Test webhook handlers with various event types
- Monitor webhook delivery success rates in dashboard
- Set up alerts for consecutive webhook failures
Troubleshooting
Webhooks Not Being Received
Webhooks Not Being Received
Check Your Configuration:
- Verify webhook URL is correct and accessible
- Ensure your server returns 2xx status codes
- Check firewall settings aren’t blocking AhaSend IPs
- Use “Send Test Event” feature in dashboard
- Test with tools like curl or Postman
- Verify your endpoint handles POST requests
- Check webhook delivery attempts in your dashboard
- Look for error messages and status codes
- Monitor retry attempts and failure patterns
Authentication Errors
Authentication Errors
Signature Verification Issues:
- Ensure webhook secret is correctly configured
- Use raw request body for signature calculation
- Check Standard Webhooks library implementation
- Using wrong webhook secret
- Modifying request body before verification
- Incorrect header name extraction
- Log incoming headers and payload
- Verify webhook secret matches dashboard
- Test with Standard Webhooks library examples
Performance Issues
Performance Issues
Timeout Problems:
- Reduce processing time in webhook handler
- Move heavy operations to background jobs
- Return 200 OK before processing starts
- Implement proper queuing systems
- Scale webhook processing horizontally
- Monitor resource usage during peak times
- Cache frequently accessed data
- Use database connection pooling
- Implement proper logging levels
Webhook Disabled
Webhook Disabled
Automatic Disabling:
- AhaSend disables webhooks after 100 consecutive failures
- You’ll receive an email notification when this happens
- Fix underlying issues before re-enabling
- Identify and resolve the root cause
- Test your endpoint is working correctly
- Re-enable the webhook in your dashboard
- Monitor webhook success rates regularly
- Set up alerts for webhook failures
- Implement proper error handling and logging
Advanced Integration Patterns
Event-Driven Architecture
Use webhooks to trigger microservices, update user interfaces, and orchestrate complex workflows based on email events.
Real-Time Analytics
Stream webhook events to analytics platforms for real-time email performance dashboards and reporting.
Customer Support Integration
Automatically create support tickets from bounce events and delivery failures to keep your team informed.
Marketing Automation
Trigger marketing campaigns, update customer segments, and personalize user experiences based on email engagement.

