Enhanced Security: Scoped credentials reduce attack surface by limiting potential damage if a credential is compromised.
Types of Scoped Credentials
AhaSend provides two distinct credential types with different scoping capabilities:Sending Credentials
SMTP & API v1/v2 sending keysDomain-scoped credentials for email sending operations only
API v2 Keys
Full API access keysAdvanced scoping with both domain restrictions and operation permissions
Sending Credentials (Domain Scoping)
Sending credentials are created from the Credentials tab and are designed specifically for email sending operations. These include SMTP credentials, API v1 keys, and API v2 sending keys.Global vs. Scoped Sending Credentials
Global Credentials (Default):- Access: Can send from any verified domain in your account
- Use case: General-purpose credentials for multi-domain applications
- Risk: Higher impact if compromised
- Access: Limited to specific domains you select
- Use case: Application-specific credentials or domain isolation
- Risk: Limited damage potential if compromised
Principle of Least Privilege: Always scope credentials to the minimum domains required for your use case.
Creating Scoped Sending Credentials
Access Credentials Tab
Navigate to sending credentials:
- Log in to your AhaSend dashboard
- Click Credentials in the main menu
- Click + Add Credential button
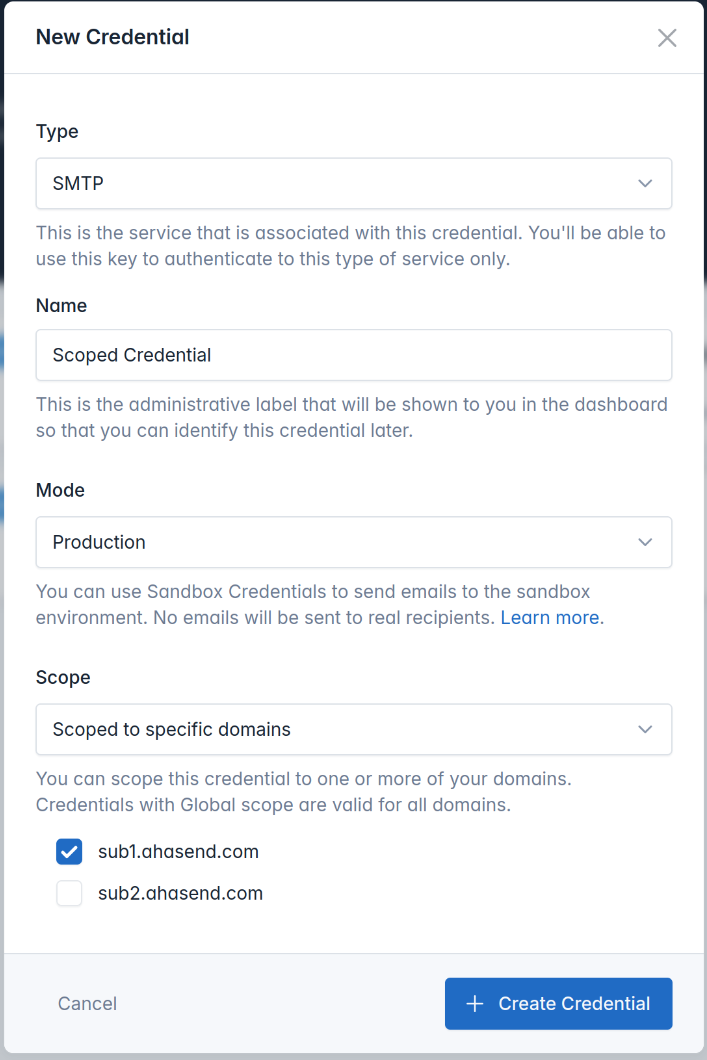
Configure Credential Details
Set up credential information:
- Type: Choose SMTP, API v1, or API v2
- Name: Enter a descriptive name
- Mode: Select Production or Sandbox
Define Domain Scope
Restrict to specific sending domains:Global Access:
- Leave Scope set to “Global” (default)
- Allows sending from any verified domain
- Select “Scope to specific domains”
- Click checkboxes for authorized domains
- Choose one or multiple domains as needed
Propagation Time: Changes to sending credentials can take up to 1 minute to propagate across all servers.
API v2 Keys (Advanced Scoping)
API v2 keys are created from Account Settings → API Keys and provide full access to the AhaSend API v2 with granular permission and domain scoping.Advanced Scoping Capabilities
API v2 keys support both domain restrictions and operation-level permissions: Domain Scoping:- Restrict API operations to specific domains
- Control which domains the key can manage or send from
- Granular control over API operations (read, write, delete)
- Resource-specific access (messages, domains, webhooks, statistics)
- Hierarchical permission inheritance
Creating API v2 Keys
Access API Keys Settings
Navigate to API key management:
- Log in to your AhaSend dashboard
- Go to Account Settings
- Click API Keys in the sidebar
- Click + Create API Key button
Configure Basic Settings
Set up API key details:
- Name: Enter a descriptive name
- Description: Optional description of the key’s purpose
Set Permission Scopes
Define what operations the key can perform:Configure specific API operation permissions based on your requirements. Common scope categories include:
- Account Management:
accounts:read,accounts:write - Message Operations:
messages:send:all,messages:read:{domain} - Domain Management:
domains:read,domains:write - Webhook Control:
webhooks:write:all,webhooks:delete:{domain}
Detailed Scoping: See our complete API scopes reference for all available permissions and syntax.
Apply Domain Restrictions
Optionally limit to specific domains:You can further restrict the API key to operate only on specific domains within your account, providing an additional layer of security.
How Sending Credential Scoping Works
When you use a domain-scoped sending credential, AhaSend validates the sending domain: SMTP Credentials:- Validates:
MAIL FROMaddress domain - Checks: Domain is in the credential’s authorized list
- Action: Refuses connection if unauthorized
- Validates:
from.emaildomain in request payload - Checks: Domain scope against the API key
- Action: Rejects request if domain is not authorized
Sending Credential Error Messages
When using credentials outside their domain scope:SMTP Authentication Error
SMTP Authentication Error
SMTP Connection Rejected:
API v1 Error
API v1 Error
API v1 Request Error:
API v2 Sending Error
API v2 Sending Error
API v2 Request Error:
API v2 Key Validation
API v2 keys undergo comprehensive validation for each request: Permission Validation:- Operation Check: Verifies the key has permission for the requested operation
- Resource Access: Ensures access to specific resources (domains, webhooks, etc.)
- Hierarchy Enforcement: Respects scope hierarchy and inheritance rules
- Resource Domain: Checks if the key can access resources for the specified domain
- Sending Domain: Validates sending permissions for message operations
API v2 Key Error Messages
When using API v2 keys outside their defined scope:Permission Scope Errors
Permission Scope Errors
Insufficient Permissions:Resource Access Denied:
Domain Scope Errors
Domain Scope Errors
Domain Not Authorized:
Advanced Permission Scoping
For granular control over API operations, API v2 keys support detailed permission scopes:Common Scope Categories
- Account Management:
accounts:read,accounts:write - Message Operations:
messages:send:all,messages:read:{domain} - Domain Management:
domains:read,domains:write - Webhook Control:
webhooks:write:all,webhooks:delete:{domain} - Statistics Access:
statistics-transactional:read:all
Scope Types
- Static Scopes: Fixed permissions like
accounts:read - Global Scopes: Domain-wide access with
:allsuffix - Domain-Specific: Restricted to particular domains using
{domain}syntax
Detailed Documentation: For complete scope definitions, validation rules, and examples, see our API Scopes Reference.
Benefits and Best Practices
Scoped credentials provide significant advantages regardless of type:Security Benefits
Enhanced Security
Enhanced Security
Minimize compromise impact:
- Limit potential damage from stolen credentials
- Reduce attack surface with principle of least privilege
- Prevent unauthorized access to sensitive domains
Improved Control
Improved Control
Granular access management:
- Separate credentials for different applications
- Team-specific permissions and domain access
- Environment-specific scoping (staging vs. production)
Error Prevention
Error Prevention
Prevent configuration mistakes:
- Block accidental sending from wrong domains
- Catch misconfigurations early in development
- Protect production domains from test applications
Easier Management
Easier Management
Simplified credential administration:
- Clear understanding of credential capabilities
- Easy revocation of specific domain access
- Organized credential structure for complex setups
Implementation Best Practices
Credential Strategy
Credential Strategy
Design your scoping approach:
- Application-specific keys: One key per application or service
- Environment separation: Different keys for staging, production
- Domain isolation: Separate keys for different business domains
- Minimal permissions: Grant only necessary scopes
Security Management
Security Management
Maintain credential security:
- Regular audit of active credentials and their scopes
- Rotate credentials periodically
- Remove unused or outdated credentials
- Monitor for scope violation errors in logs
Development Workflow
Development Workflow
Integrate scoping into development:
- Use scoped credentials in development environments
- Test scope restrictions before production deployment
- Document credential requirements for each application
- Implement proper error handling for scope violations
Common Use Cases
Multi-Tenant SaaS
Customer domain isolationCreate domain-scoped credentials for each customer’s subdomain, preventing cross-customer access
Microservices Architecture
Service-specific credentialsEach microservice gets credentials scoped to its required domains and operations
Marketing & Transactional
Purpose-based separationSeparate credentials for marketing emails vs. transactional notifications
Third-Party Integrations
External service limitationsProvide limited-scope credentials to external services and partners

